Why a Charge Controller is necessary
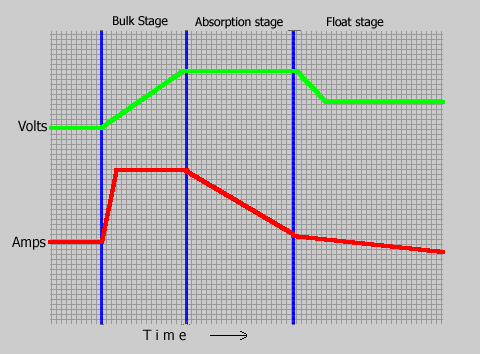
The relationship between the current and the voltage during the 3 phases of the charge cycle can be shown visually by the graph below.
| MPPT Maximum Power Point Tracking | |
| Most multi-stage charge controllers are Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) types. I would recommend using one of at least this design. The newer Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) controllers are even better. They match the output of the solar panels to the battery voltage to insure maximum charge (amps). For example: even though your solar panel is rated at 100 watts, you won't get the full 100 watts unless the battery is at optimum voltage. The Power/Watts is always equal to Volts times Amps or P=E*I (see Ohm´s Law for more info). With a regular charge controller, if your batteries are low at say 12.4 volts, then your 100 watt solar panel rated at 6 amps at 16.5 volts (6 amps times 16.5 volts = 100 watts) will only charge at 6 amps times 12.4 volts or just 75 watts. You just lost 25% of your capacity! The MPPT controller compensates for the lower battery voltage by delivering closer to 8 amps into the 12.4 volt battery maintaining the full power of the 100 watt solar panel! 100 watts = 12.4 volts times 8 amps = 100 (P=E*I). | |
| The Charge Controller is installed between the Solar Panel array and the Batteries where it automatically maintains the charge on the batteries using the 3 stage charge cycle just decribed. The Power Inverter can also charge the batteries if it is connected to the AC utility grid or in the case of a stand alone system, your own Ac-generators | |
Ohm´s Law
Voltage : is the electromotive force (pressure) applied to an electrical circuit measured in volts (E).
Current : is the flow of electrons in an electrical circuit measured in amperes (I).
Resistance : is the opposition to the flow...
Contact Us
Newsletter
Subscribe to daily newsletter:

